Message Passing in Chrome Extension MV3
Chrome Extension + Chrome Messaging + Promise & Async Operations
- Between Background and Popup scripts
- Between Background and Content scripts
- Between Popup and Content scripts
- Some Gotchas!
A chrome extension is made up of multiple components, each with its own scope/functionality regarding what it can do in the browser. Example,
-
Background script: Listen to events happening in the extension, which covers all Chrome windows. -
Popup script: A web page that knows information about Chrome tabs. -
Content script: Read and modify the DOM of the current web page in the browser.
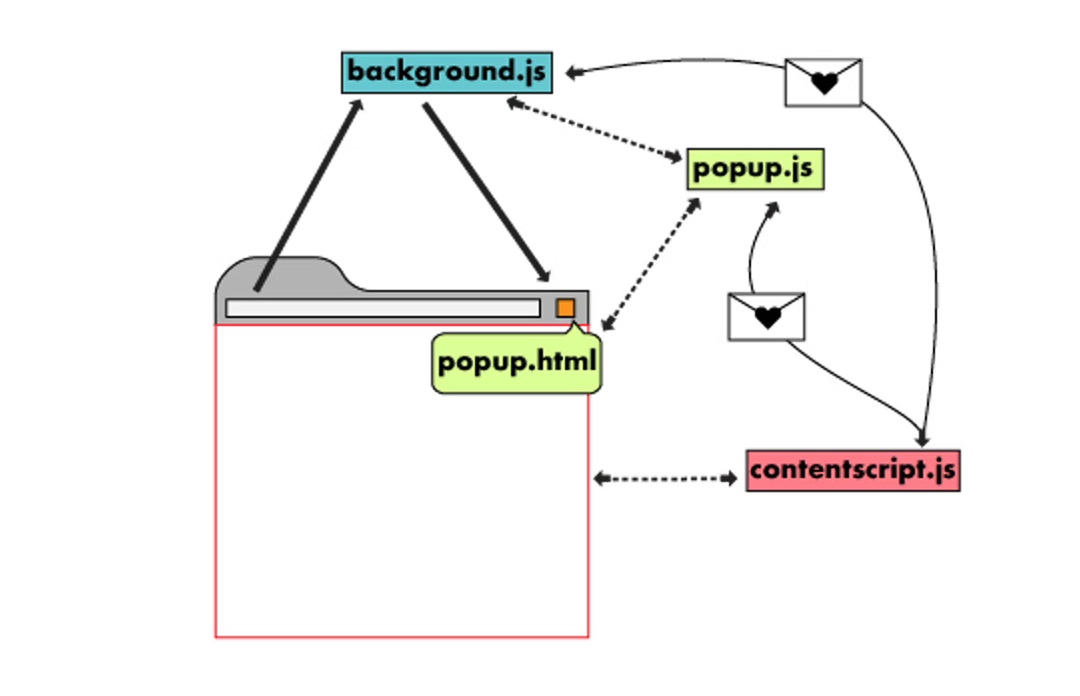 Ref: Chrome Extension Architecture
Ref: Chrome Extension Architecture
As each has its own scope, chrome extensions may or may not require information on each scope depending on the use case. Through chrome’s message passing, you can move information from one scope to another.
Here’s how each message looks consolidated.
- You will need a listener:
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener - Depending on who is sending the message and to where, use :
chrome.tabs.sendMessagechrome.runtime.sendMessage
Between Background and Popup scripts
Popup to Background
popup.js
//Sending message
chrome.runtime.sendMessage({ message: 'user_signed_in', payload: confirmState },
// callback response to the request
function (response) {
if (response.message === 'success' && confirmState) {
//user is signed in , do something
}
}
);
background.js
//Listening to Messages
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(function (request, sender, sendResponse) {
if (request.message === 'user_signed_in') {
// do something
//callback reponse sent
sendResponse({ message: 'success' });
}
return true;
});
Background to Popup
background.js
chrome.runtime.sendMessage({
msg: "something_completed",
data: {
subject: "Loading",
content: "Just completed!"
}
});
popup.js
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(
function(request, sender, sendResponse) {
if (request.msg === "something_completed") {
// To do something
console.log(request.data.subject)
console.log(request.data.content)
}
}
);
Ref: Stackoverflow Link
Between Background and Content scripts
Content to Background
content.js
chrome.runtime.sendMessage({greeting: "hello"}, function(response) {
console.log(response.farewell);
});
background.js
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(
function(request, sender, sendResponse) {
console.log(sender.tab ?
"from a content script:" + sender.tab.url :
"from the extension");
if (request.greeting === "hello")
sendResponse({farewell: "goodbye"});
}
);
Background to Content
background.js
chrome.tabs.query({active: true, currentWindow: true}, function(tabs){
const activeTab= tabs[0]
//Sending message to active Tab
chrome.tabs.sendMessage(activeTab.id, { message: "start" },
//callback response
function (response) {
if (response.message === 'success') {
console.log("success!!")
}
}
);
};
content.js
//Listening to Messages
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(function (request, sender, sendResponse) {
if (request.message === 'start') {
//callback response to request
sendResponse({ message : 'success' });
}
return true;
});
Between Popup and Content scripts
Popup to Content
popup.js
chrome.tabs.query({active: true, currentWindow: true}, function(tabs){
let activeTab = tabs[0];
//Sending message to active Tab
chrome.tabs.sendMessage(activeTab.id,{ message: 'get_details' },
//callback
function (response) {
if (response.message === 'success') {
console.log("success!!")
}
});
})
content.js
//Listening to Messages
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(function (request, sender, sendResponse) {
if (request.message === 'get_details') {
//callback response to request
sendResponse({ message : 'success' });
}
return true;
});
Content to Popup
content.js
chrome.runtime.sendMessage({greeting: "hello"}, function(response) {
console.log(response.farewell);
});
popup.js
chrome.runtime.onMessage.addListener(
function(request, sender, sendResponse) {
console.log(sender.tab ?
"from a content script:" + sender.tab.url :
"from the extension");
if (request.greeting === "hello")
sendResponse({farewell: "goodbye"});
}
);
Some Gotchas!
Sync and Async Operations
- The
sendResponsein the Content to Popup implementation is behaving synchronous. - To use
sendReponseasynchronously, usereturn true;as in the Popup to Content implementation.
Promises
If you are waiting on some callback function result which is asynchronous, you can wrap the operation in a promise.
Example, waiting on the getting active tab information from chrome.tabs, to send the message from background to content. Without a promise, the message response may not be captured by background. Make the changes like below:
//Follow Promise style
function getActiveTab() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
chrome.tabs.query({
active: true,
currentWindow: true
}, function (tabs) {
resolve(tabs[0]);
});
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
})
}
let activeTabPromise = getActiveTab()
Promise.all([activeTabPromise])
.then(result => {
const activeTab = result[0]
//Sending message to active Tab
chrome.tabs.sendMessage(activeTab.id, { message: "start" },
//callback response
function (response) {
if (response.message === 'success') {
console.log("success!!")
}
}
);
});